Cranial nerves
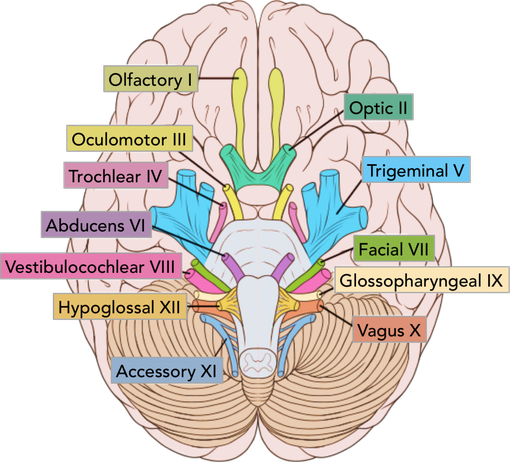
The cranial nerves are a set of 12 paired nerves that arise directly from the brain. The first two nerves (olfactory and optic) arise from the cerebrum, whereas the remaining ten emerge from the brain stem.
The names of the cranial nerves relate to their function and they are also numerically identified in roman numerals (I-XII).
There are twelve cranial nerves in total. The olfactory nerve (CN I) and optic nerve (CN II) originate from the cerebrum. Cranial nerves III – XII arise from the brain stem. They can arise from a specific part of the brain stem (midbrain, pons or medulla), or from a junction between two parts:
- Midbrain – the trochlear nerve (IV) comes from the posterior side of the midbrain. It has the longest intracranial length of all the cranial nerves.
- Midbrain-pontine junction – oculomotor (III).
- Pons – trigeminal (V).
- Pontine-medulla junction – abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear (VI-VIII).
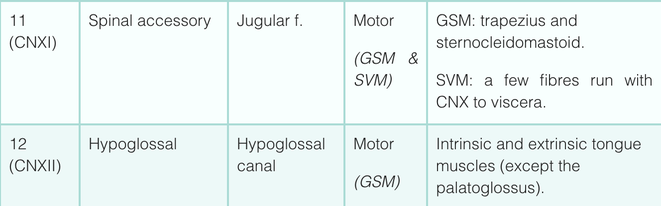
- Medulla Oblongata – posterior to the olive: glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory (IX-XI). Anterior to the olive: hypoglossal (XII).
The cranial nerves are numbered by their location on the brain stem (superior to inferior, then medial to lateral) and the order of their exit from the cranium (anterior to posterior)
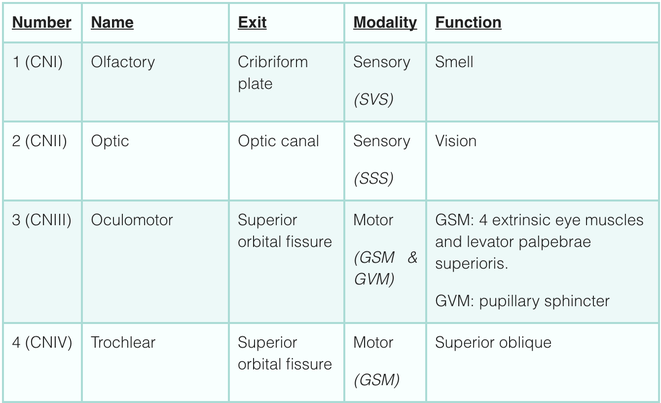
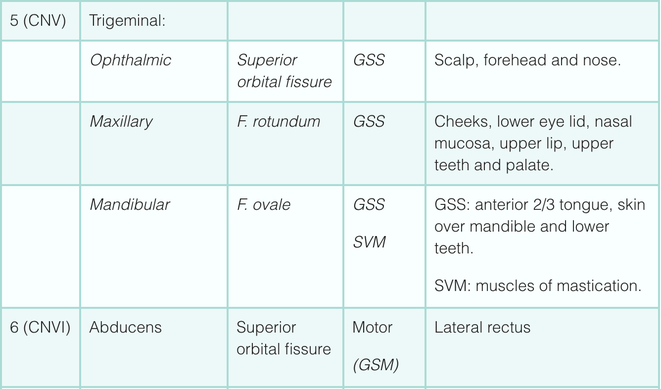
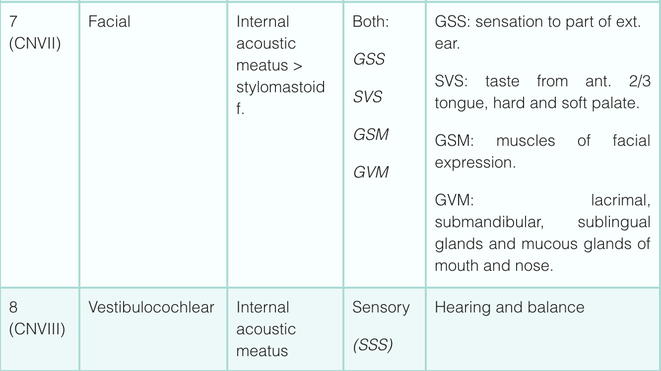
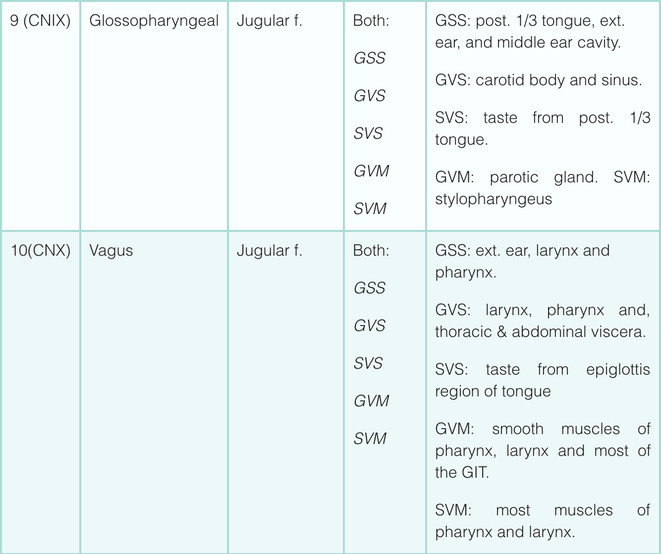
Simplistically, each cranial nerve can be described as being sensory, motor or both. They can more specifically transmit seven types of information; three are unique to cranial nerves (SSS, SVS and SVM).
Sensory (afferent) Modalities:
- General somatic sensory (GSS) – general sensation from skin.
- General visceral sensory (GVS) – general sensation from viscera.
- Special somatic sensory (SSS) – senses derived from ectoderm (sight, sound, balance).
- Special visceral sensory (SVS) – senses derived from endoderm (taste).
Motor (efferent) Modalities:
- General somatic motor (GSM) – skeletal muscles.
- General visceral motor (GVM) – smooth muscles of gut and autonomic motor.
- Special visceral motor (SVM) – muscles derived from pharyngeal arches.